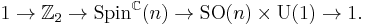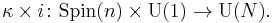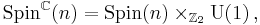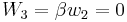Spin structure
In differential geometry, a spin structure on an orientable Riemannian manifold 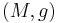 allows one to define associated spinor bundles, giving rise to the notion of a spinor in differential geometry.
allows one to define associated spinor bundles, giving rise to the notion of a spinor in differential geometry.
Spin structures have wide applications to mathematical physics, in particular to quantum field theory where they are an essential ingredient in the definition of any theory with uncharged fermions. They are also of purely mathematical interest in differential geometry, algebraic topology, and K theory. They form the foundation for spin geometry.
Contents |
Introduction
In geometry, as well as in field theory, given an oriented Riemannian manifold 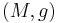 one wishes that it admits spinors. A method for dealing with this problem is to require that
one wishes that it admits spinors. A method for dealing with this problem is to require that  has a spin structure.[1][2][3][4] There is a topological obstruction to the existence of spin structures on a Riemannian manifold
has a spin structure.[1][2][3][4] There is a topological obstruction to the existence of spin structures on a Riemannian manifold 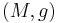 . Such structures will exist if and only if the second Stiefel-Whitney class
. Such structures will exist if and only if the second Stiefel-Whitney class 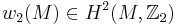 of
of  vanishes. Furthermore, if
vanishes. Furthermore, if 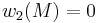 , then the set of the isomorphism classes of spin structures on
, then the set of the isomorphism classes of spin structures on  is acted upon freely and transitively by
is acted upon freely and transitively by 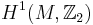 . As the manifold
. As the manifold  is assumed to be oriented, the first Stiefel-Whitney class
is assumed to be oriented, the first Stiefel-Whitney class 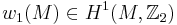 of
of  vanishes too. (The Stiefel-Whitney classes
vanishes too. (The Stiefel-Whitney classes 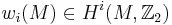 of a manifold
of a manifold  are defined to be the Stiefel-Whitney classes of its tangent bundle
are defined to be the Stiefel-Whitney classes of its tangent bundle 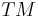 .)
.)
The bundle of spinors 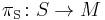 over
over  is then the complex vector bundle associated to the corresponding principal bundle
is then the complex vector bundle associated to the corresponding principal bundle 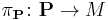 of spin frames over
of spin frames over  and the spin representation of its structure group
and the spin representation of its structure group 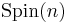 on the space of spinors
on the space of spinors 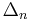 . The bundle
. The bundle 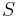 is called the spinor bundle for a given spin structure on
is called the spinor bundle for a given spin structure on  .
.
A precise definition of spin structure on manifold was possible only after the notion of fiber bundle had been introduced; André Haefliger (1956) found the topological obstruction to the existence of a spin structure on an orientable Riemannian manifold and Max Karoubi (1968) extended this result to the non-orientable pseudo-Riemannian case.
Spin structures on Riemannian manifolds
Definition
A spin structure on an orientable Riemannian manifold 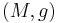 is an equivariant lift of the oriented orthonormal frame bundle
is an equivariant lift of the oriented orthonormal frame bundle 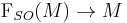 with respect to the double covering
with respect to the double covering 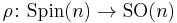 . In other words, a pair
. In other words, a pair 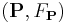 is a spin structure on the principal bundle
is a spin structure on the principal bundle 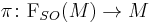 when
when
- a)
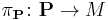 is a principal
is a principal 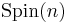 -bundle over
-bundle over  ,
, - b)
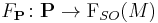 is an equivariant
is an equivariant 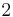 -fold covering map such that
-fold covering map such that
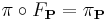 and
and 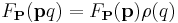 for all
for all 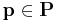 and
and 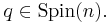
The principal bundle 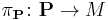 is also called the bundle of spin frames over
is also called the bundle of spin frames over  .
.
Two spin structures 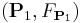 and
and 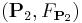 on the same oriented Riemannian manifold
on the same oriented Riemannian manifold 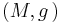 are called equivalent if there exists a
are called equivalent if there exists a 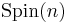 -equivariant map
-equivariant map 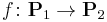 such that
such that
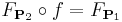 and
and  for all
for all 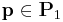 and
and 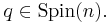
Of course, in this case 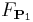 and
and 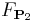 are two equivalent double coverings of the oriented orthonormal frame
are two equivalent double coverings of the oriented orthonormal frame 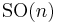 -bundle
-bundle 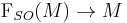 of the given Riemannian manifold
of the given Riemannian manifold 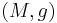 .
.
This definition of spin structure on 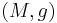 as a spin structure on the principal bundle
as a spin structure on the principal bundle 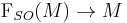 is due to André Haefliger (1956).
is due to André Haefliger (1956).
Obstruction
André Haefliger [1] found necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of a spin structure on an oriented Riemannian manifold 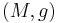 . The obstruction to having a spin structure is certain element
. The obstruction to having a spin structure is certain element ![[k]\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8cd6a6231f2025a9d81df5925dba55b3.png) of
of 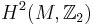 . For a spin structure the class
. For a spin structure the class ![[k]\,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8cd6a6231f2025a9d81df5925dba55b3.png) is the second Stiefel-Whitney class
is the second Stiefel-Whitney class 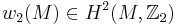 of
of  . Hence, a spin structure exists if and only if the second Stiefel-Whitney class
. Hence, a spin structure exists if and only if the second Stiefel-Whitney class 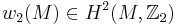 of
of  vanishes.
vanishes.
Spin structures on vector bundles
Let M be a paracompact topological manifold and E an oriented vector bundle on M of dimension n equipped with a fibre metric. This means that at each point of M, the fibre of E is an inner product space. A spinor bundle of E is a prescription for consistently associating a spin representation to every point of M. There are topological obstructions to being able to do it, and consequently, a given bundle E may not admit any spinor bundle. In case it does, one says that the bundle E is spin.
This may be made rigorous through the language of principal bundles. The collection of oriented orthonormal frames of a vector bundle form a frame bundle PSO(E), which is a principal bundle under the action of the special orthogonal group SO(n). A spin structure for PSO(E) is a lift of PSO(E) to a principal bundle PSpin(E) under the action of the spin group Spin(n), by which we mean that there exists a bundle map φ : PSpin(E) → PSO(E) such that
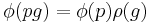 , for all p ∈ PSpin(E) and g ∈ Spin(n),
, for all p ∈ PSpin(E) and g ∈ Spin(n),
where 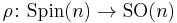 is the mapping of groups presenting the spin group as a double-cover of SO(n).
is the mapping of groups presenting the spin group as a double-cover of SO(n).
In the special case in which E is the tangent bundle 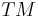 over the base manifold
over the base manifold  , if a spin structure exists then one says that M is a spin manifold. Equivalently M is spin if the SO(n) principal bundle of orthonormal bases of the tangent fibers of M is a Z2 quotient of a principal spin bundle.
, if a spin structure exists then one says that M is a spin manifold. Equivalently M is spin if the SO(n) principal bundle of orthonormal bases of the tangent fibers of M is a Z2 quotient of a principal spin bundle.
If the manifold has a cell decomposition or a triangulation, a spin structure can equivalently be thought of as a homotopy-class of trivialization of the tangent bundle over the 1-skeleton that extends over the 2-skeleton. If the dimension is lower than 3, one first takes a Whitney sum with a trivial line bundle.
Obstruction
A spin structure on a vector bunddle E exists if and only if the second Stiefel-Whitney class w2 of E vanishes. This is a result of Armand Borel and Friedrich Hirzebruch.[5] Note, we have assumed 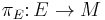 is an orientable vector bundle.
is an orientable vector bundle.
Classification
When spin structures exist, the inequivalent spin structures on a manifold have a one-to-one correspondence (not canonical) with the elements of H1(M,Z2), which by the universal coefficient theorem is isomorphic to H1(M,Z2). More precisely, the space of the isomorphism classes of spin structures is an affine space over H1(M,Z2).
Intuitively, for each nontrivial cycle on M a spin structure corresponds to a binary choice of whether a section of the SO(N) bundle switches sheets when one encircles the loop. If w2 vanishes then these choices may be extended over the two-skeleton, then (by obstruction theory) they may automatically be extended over all of M. In particle physics this corresponds to a choice of periodic or antiperiodic boundary conditions for fermions going around each loop.
Application to particle physics
In particle physics the spin statistics theorem implies that the wavefunction of an uncharged fermion is a section of the associated vector bundle to the spin lift of an SO(N) bundle E. Therefore the choice of spin structure is part of the data needed to define the wavefunction, and one often needs to sum over these choices in the partition function. In many physical theories E is the tangent bundle, but for the fermions on the worldvolumes of D-branes in string theory it is a normal bundle.
Examples
- A genus g Riemann surface admits 22g inequivalent spin structures; see theta characteristic.
- The complex projective plane CP2 is not spin.
- All even dimensional complex projective spaces CP2n are not spin
- All odd dimensional complex projective spaces CP2n+1 are spin
- All compact, orientable manifolds of dimension 3 or less are spin.
- All Calabi-Yau manifolds are spin.
Properties
- The  genus of a spin manifold is an integer, and is an even integer if in addition the dimension is 4 mod 8.
- In general the  genus is a rational invariant, defined for any manifold, but it is not in general an integer.
- This was originally proven by Hirzebruch and Borel, and can be proven by the Atiyah–Singer index theorem, by realizing the  genus as the index of a Dirac operator – a Dirac operator is a square root of a second order operator, and exists due to the spin structure being a "square root". This was a motivating example for the index theorem.
Spinc structures
A spinc structure is analogous to a spin structure on an oriented Riemannian manifold,[6] but uses the spinc group, which is defined instead by the exact sequence
To motivate this, suppose that 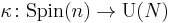 is a complex spinor representation. The center of
is a complex spinor representation. The center of 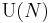 consists of the diagonal elements coming from the inclusion
consists of the diagonal elements coming from the inclusion 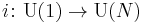 , i.e., the scalar multiples of the identity. Thus there is a homomorphism
, i.e., the scalar multiples of the identity. Thus there is a homomorphism
This will always have the element (-1,-1) in the kernel. Taking the quotient modulo this element gives the group 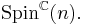 This is the twisted product
This is the twisted product
where 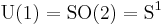 . In other words, the group Spinc(n) is a central extension of SO(n) by S1.
. In other words, the group Spinc(n) is a central extension of SO(n) by S1.
Viewed another way, Spinc(n) is the quotient group obtained from 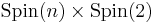 with respect to the normal
with respect to the normal 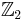 which is generated by the pair of covering transformations for the bundles
which is generated by the pair of covering transformations for the bundles 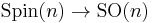 and
and 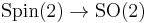 respectively. This makes the spinc group both a bundle over the circle with fibre
respectively. This makes the spinc group both a bundle over the circle with fibre 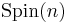 , and a bundle over
, and a bundle over 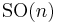 with fibre a circle.[7][8]
with fibre a circle.[7][8]
The fundamental group 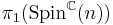 is isomorphic to
is isomorphic to 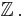
If the manifold has a cell decomposition or a triangulation, a spinc structure can be equivalently thought of as a homotopy class of complex structure over the 2-skeleton that extends over the 3-skeleton. Similarly to the case of spin structures, one takes a Whitney sum with a trivial line bundle if the manifold is odd dimensional.
Yet another definition is that a spinc structure on a manifold 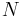 is a complex line bundle
is a complex line bundle 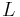 over
over 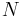 together with a spin structure on
together with a spin structure on 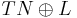 .
.
Obstruction
A spinc structure exists when the bundle is orientable and the second Stiefel-Whitney class of the bundle E is in the image of the map 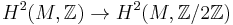 (in other words, the third integral Stiefel-Whitney class vanishes). In this case one says that E is spinc. Intuitively, the lift gives the Chern class of the square of the U(1) part of any obtained spinc bundle.
(in other words, the third integral Stiefel-Whitney class vanishes). In this case one says that E is spinc. Intuitively, the lift gives the Chern class of the square of the U(1) part of any obtained spinc bundle.
Classification
When a manifold carries a spinc structure at all, the set of spinc structures forms an affine space. Moreover, the set of spinc structures has a free transitive action of 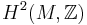 . Thus, spinc-structures correspond to elements of
. Thus, spinc-structures correspond to elements of 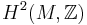 although not in a natural way.
although not in a natural way.
Geometric picture
This has the following geometric interpretation, which is due to Edward Witten. When the spinc structure is nonzero this square root bundle has a non-integral Chern class, which means that it fails the triple overlap condition. In particular, the product of transition functions on a three-way intersection is not always equal to one, as is required for a principal bundle. Instead it is sometimes −1.
This failure occurs at precisely the same intersections as an identical failure in the triple products of transition functions of the obstructed spin bundle. Therefore the triple products of transition functions of the full spinc bundle, which are the products of the triple product of the spin and U(1) component bundles, are either 12=1 or -12=1 and so the spinc bundle satisfies the triple overlap condition and is therefore a legitimate bundle.
The details
The above intuitive geometric picture may be made concrete as follows. Consider the short exact sequence 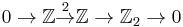 where the second arrow is multiplication by 2 and the third is reduction modulo 2. This induces a long exact sequence on cohomology, which contains
where the second arrow is multiplication by 2 and the third is reduction modulo 2. This induces a long exact sequence on cohomology, which contains
where the second arrow is induced by multiplication by 2, the third is induced by restriction modulo 2 and the fourth is the associated Bockstein homomorphism β.
The obstruction to the existence of a spin bundle is an element w2 of H2(M,Z2). It reflects the fact that one may always locally lift an SO(N) bundle to a spin bundle, but one needs to choose a Z2 lift of each transition function, which is a choice of sign. The lift does not exist when the product of these three signs on a triple overlap is -1, which yields the Čech cohomology picture of w2.
To cancel this obstruction, one tensors this spin bundle with a U(1) bundle with the same obstruction w2. Notice that this is an abuse of the word bundle, as neither the spin bundle nor the U(1) bundle satisfies the triple overlap condition and so neither is actually a bundle.
A legitimate U(1) bundle is classified by its Chern class, which is an element of H2(M,Z). Identify this class with the first element in the above exact sequence. The next arrow doubles this Chern class, and so legitimate bundles will correspond to even elements in the second H2(M,Z), while odd elements will correspond to bundles that fail the triple overlap condition. The obstruction then is classified by the failure of an element in the second H2(M,Z) to be in the image of the arrow, which, by exactness, is classified by its image in H2(M,Z2) under the next arrow.
To cancel the corresponding obstruction in the spin bundle, this image needs to be w2. In particular, if w2 is not in the image of the arrow, then there does not exist any U(1) bundle with obstruction equal to w2 and so the obstruction cannot be cancelled. By exactness, w2 is in the image of the preceding arrow only if it is in the kernel of the next arrow, which we recall is the Bockstein homomorphism β. That is, the condition for the cancellation of the obstruction is
where we have used the fact that the third integral Stiefel-Whitney class W3 is the Bockstein of the second Stiefel-Whitney class w2 (this can be taken as a definition of W3).
Integral lifts of Stiefel-Whitney classes
This argument also demonstrates that second Stiefel-Whitney class defines elements not only of Z2 cohomology but also of integral cohomology in one higher degree. In fact this is the case for all even Stiefel-Whitney classes. It is traditional to use an uppercase W for the resulting classes in odd degree, which are called the integral Stiefel-Whitney classes, and are labeled by their degree (which is always odd).
Application to particle physics
In quantum field theory charged spinors are sections of associated spinc bundles, and in particular no charged spinors can exist on a space that is not spinc. An exception arises in some supergravity theories where additional interactions imply that other fields may cancel the third Stiefel-Whitney class.
Examples
- All oriented smooth manifolds of dimension 4 or less are spinc.[9]
- All almost complex manifolds are spinc.
- All spin manifolds are spinc.
Vector structures
While spin structures are lifts of vector bundles to associated spin bundles, vector structures are lifts of other bundles to associated vector bundles.
Obstruction
For example, consider an SO(8) bundle. The group SO(8) has three 8-dimensional representations, two of which are spinorial and one of which is the vector representation. These three representations are exchanged by an isomorphism known as triality. Given an SO(8) vector bundle E, the obstruction to the construction of an associated spin bundle is the second Stiefel-Whitney class w2(E), which is an element of the second cohomology group with Z2 coefficients. By triality, given an SO(8) spin bundle F, the obstruction to the existence of an associated vector bundle is another element of the same cohomology group, which is often denoted 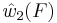 .
.
Application to particle physics
Vector structures were first considered in physics, in the paper Anomalies, Dualities and Topology of D=6, N=1 Superstring Vacua by Micha Berkooz, Robert Leigh, Joseph Polchinski, John Schwarz, Nathan Seiberg and Edward Witten. They were considering type I string theory, whose configurations consist of a 10-manifold with a Spin(32)/Z2 principle bundle over it. Such a bundle has a vector structure, and so lifts to an SO(32) bundle, when the triple product of the transition functions on all triple intersection is the trivial element of the Z2 quotient. This happens precisely when 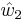 , the characteristic 2-cocycle with Z2 coefficients, vanishes.
, the characteristic 2-cocycle with Z2 coefficients, vanishes.
The following year, in The Mirror Transform of Type I Vacua in Six Dimensions, Ashoke Sen and Savdeep Sethi demonstrated that type I superstring theory is only consistent, in the absence of fluxes, when this characteristic class is trivial. More generally, in type I string theory the B-field is also a class in the second cohomology with Z2 coefficients and they demonstrated that it must be equal to 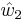 .
.
See also
References
- ^ a b A. Haefliger (1956). "Sur l’extension du groupe structural d’un espace fibré". C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 243: 558–560.
- ^ J. Milnor (1963). "Spin structures on manifolds". L'Enseignement Math. 9: 198–203.
- ^ A. Lichnerowicz (1964). "Champs spinoriels et propagateurs en rélativité générale". Bull. Soc. Math. Fr. 92: 11–100.
- ^ M. Karoubi (1968). "Algèbres de Clifford et K-théorie". Ann. Sci. Éc. Norm. Sup. 1 (2): 161–270.
- ^ A. Borel; F. Hirzebruch (1958). "Characteristic classes and homogeneous spaces I". American Journal of Mathematics 80 (2): 97–136. doi:10.2307/2372795. JSTOR 2372795.
- ^ Lawson, H. Blaine; Michelsohn, Marie-Louise (1989). Spin Geometry. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-08542-5 page 391
- ^ R. Gompf (1997). "Spinc–structures and homotopy equivalences". Geometry & Topology 1: 41–50. doi:10.2140/gt.1997.1.41.
- ^ Friedrich, Thomas (2000). Dirac Operators in Riemannian Geometry. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 978-0-8218-2055-1 page 26
- ^ Gompf, Robert E.; Stipsicz, Andras I. (1999). 4-Manifolds and Kirby Calculus. American Mathematical Society. pp. 55–58, 186–187. ISBN 0-8218-0994-6.
Books
- Lawson, H. Blaine; Michelsohn, Marie-Louise (1989). Spin Geometry. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-08542-5
- Friedrich, Thomas (2000). Dirac Operators in Riemannian Geometry. American Mathematical Society. ISBN 978-0-8218-2055-1
Further reading
- Something on Spin Structures by Sven-S. Porst is a short introduction to orientation and spin structures for mathematics students.